
Explore how air pollution impacts the environment & which are the greenest places to travel to!
Air pollution is the second largest risk factor of death and kills an estimated seven million people worldwide each year. According to the EPA, 67 million tons of pollution were released into the atmosphere by the US in 2021. Fine particle matter is one pollutant which is particularly harmful to the public, as fine particles can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, enter the bloodstream and cause damage to organs, tissues, and cells.
Travel contributes to air pollution, but there are ways you can offset your carbon footprint and opt for visiting destinations which have less air pollution. Even being subjected to air pollution for a short period of time can cause breathing difficulties when travelling and it’s estimated that UK holidaymakers spend over £998 million a year buying over-the-counter treatments for respiratory or allergy-related illnesses on holiday.
So where are the safest places to visit? Find out below..
Top Air Pollution Statistics 2024
In 2023, global carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels reached a record high of 37.4 billion tons, an increase of 1.1% from 2022.
This is a 1.5% increase from pre-pandemic levels.
When other sources are included, total emissions in 2023 are estimated to have been 40.9 billion metric tons.
Between 1980 and 2022, CO₂ emissions dropped by 73% in the United States.
Nearly 97 million people in the United States live in counties with air pollution concentrations above the National Ambient Air Quality Standards.
Indoor and outdoor pollution contributed to 11.6% of global deaths in 2019.
They kill 6.6 million people annually.
An estimated 716 million of the world's lowest-income people live in areas with unsafe levels of air pollution.
The global air pollution death rate has declined by about 45% over the last three decades.
Air pollution resulting from cars and buses contributes to one in ten deaths globally.
According to data from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), prior to COVID-19, nearly one in four Americans resided in counties with poor air quality.
Air pollution is estimated to kill 7 million people every year.
In the UK, the impact of air pollution is estimated by the Government to be equivalent to between 28,000 and 36,000 premature deaths per year.
Air pollutants with the strongest evidence for impacting public health include, particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and Sulphur dioxide (SO2). Fine particulate matter is especially harmful to health, as these tiny particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, enter the bloodstream, and travel to organs, subsequently causing systemic damages to tissues and cells.
Sources: SustainableJungle, EPA, Reason, Downtoearth, Vox, Human Rights Careers, BBC, Washington Examiner, UCEM, FilterBuy, Brittanica, LSE
85% of all global air pollution comes from burning fossil fuels and biomass.
- Coal-fired power stations alone account for 35% of harmful mercury emissions in the US.
- Two-thirds of SO2 emissions cause acid rain.
- The great majority of dust (particle pollution) is released in our air due to fossil fuel burning.
Industrial Emission
- 59% of greenhouse gas emissions in the EU in 2021.
- 32% of ozone precursor emissions in the EU in 2021.
- 29% of particulates smaller than 2.5 µm in the EU in 2021.
- Large global companies are responsible for at least 50% of all greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
Indoor Air Pollution
- 17% of deaths from lung cancer are caused by carcinogens and toxins from indoor air pollution.
- According to WHO, Pneumonia is the cause of 27% of yearly deaths attributed to indoor air pollution.
- Plus 45% of all pneumonia deaths in children under five years old.
- In 2020, household air pollution was predicted to be responsible for 3.2 million deaths per year, including approximately 2,37,000 deaths of children under the age of five.
Wildfires
- 90% of the wildfires are caused by humans.
- Soot and dust particles, that contain several toxic chemicals can stay in the air for days.
Microbial Decaying Process
- In the US, manufacturing accounts for 23% of direct carbon emissions, and globally, it accounts for 12% of greenhouse gas emissions.
- In the United States, manufacturing accounts for 23% of direct carbon emissions, and globally, it accounts for 12% of greenhouse gas emissions.
- The industry also uses 54% of the world's energy, and some of the machines used in manufacturing run on coal, oil, or gas.
Transportation
- Transport is responsible for roughly 25% of the EU's total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and causes air pollution, noise pollution and habitat fragmentation.
- It is the largest sector that emits greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the UK and US, accounting for 26% and 28% of total emissions, (2021 & 2022).
- Transport is responsible for 32% of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and 14% of particulate matter less than 2.5 micrometres across (PM2.5) emissions.
Open Burning of Garbage Waste
- Burning waste produces 29% of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution in the air, and 11% of global black carbon emissions.
- Waste mismanagement is estimated to be responsible for 400,000–1,000,000 deaths globally each year.
- Plastic waste may be responsible for a significant portion of these deaths.
- The air pollutants created by open burning can cause nearly 1.2 million premature deaths per year in Africa.
Construction and Demolition
- According to some studies, construction is responsible for up to 50% of climate change.
- This sector accounted for 37% of global greenhouse gas emissions, 34% of energy demand, and 40% of energy and carbon dioxide emissions in 2021.
- It contributes to 23% of air pollution, 40% of drinking water pollution and 50% of landfill wastes.
Agricultural Activities
- About 40% of world emissions come from livestock
- 16% from mineral fertilizers
- 17% from burning biomass
- 8% come from agricultural wastes.
Use of chemical and synthetic products
Household products cause indoor air pollution which is 10 times more harmful than outdoor air pollution. Around 47% of the world’s population - 3.6 billion people, are exposed to household air pollution from the burning of solid fuels for cooking.
- Candles
- Air Freshener
- Household Cleaning Products
- Paint
140 million people nationwide lived in counties with pollution levels above the primary NAAQS in 2023.
The highest average exposure rates for ambient particulate matter air pollution were seen in Qatar, Egypt, and Bahrain.
9 out of 10 deaths attributed to outdoor air pollution are in low- and middle-income countries.
Worst cities for air pollution
The 10 most polluted countries with the worst air quality are in South and Central Asia.
Bangladesh took the top spot, with more than 15 times higher than safe standards, and Pakistan came in second, with levels 14 times above safe levels.
Dhaka, Bangladesh (114.5 µg/m3)
Lahore, Pakistan (95.1 µg/m3)
Patna, India (67.0 µg/m3)
New Delhi, India (65.9 µg/m3)
Delhi, India (64.0 µg/m3)
Urumqi, China (63.4 µg/m3)
Muzaffarnagar, India (62.4 µg/m3)
Xi’an, China (57.9 µg/m3)
Xuchang, China (57.0 µg/m3)
Peshawar, Pakistan (56.2 µg/m3)
The most polluted city in Europe is Igdir in Turkey, with PM2.5 levels over 9 times the safe standard.
The most polluted city in America is Bakersfield, California with 16 micrograms of fine particulate pollution per cubic meter.
Los Angeles has the worst ozone pollution, or smog.
Best Cities for Air Pollution
Only seven countries in the world met safe air pollution levels of five micrograms per cubic metre of air (µg/m3) or less in 2023.
The best cities around the world for air quality are:
Zürich, Switzerland (0.4 µg/m3)
Perth, Australia (1.5 µg/m3)
Hobart, Australia (2.3 µg/m3)
Uppsala, Sweden (3.5 µg/m3)
Launceston, Australia (3.5 µg/m3)
Reykjavík, Iceland (4.0 µg/m3)
Tampere, Finland (4.0 µg/m3)
Turku, Finland (4.1 µg/m3)
Vancouver, Canada (4.3 µg/m3)
Wollongong, Australia (4.4 µg/m3)
Air pollution in some of the top travel destinations
As of August 9, 2024, Jersey's Air Quality Index (AQI) was 21, which is considered good.
Guernsey’s Air Quality Index (AQI) was 30, also rated as good.
Sources: IQAir, EPA, Health Data, Lung Association, Clean Air Fund, Euro News, Smart Air Filters, AQI, BBC
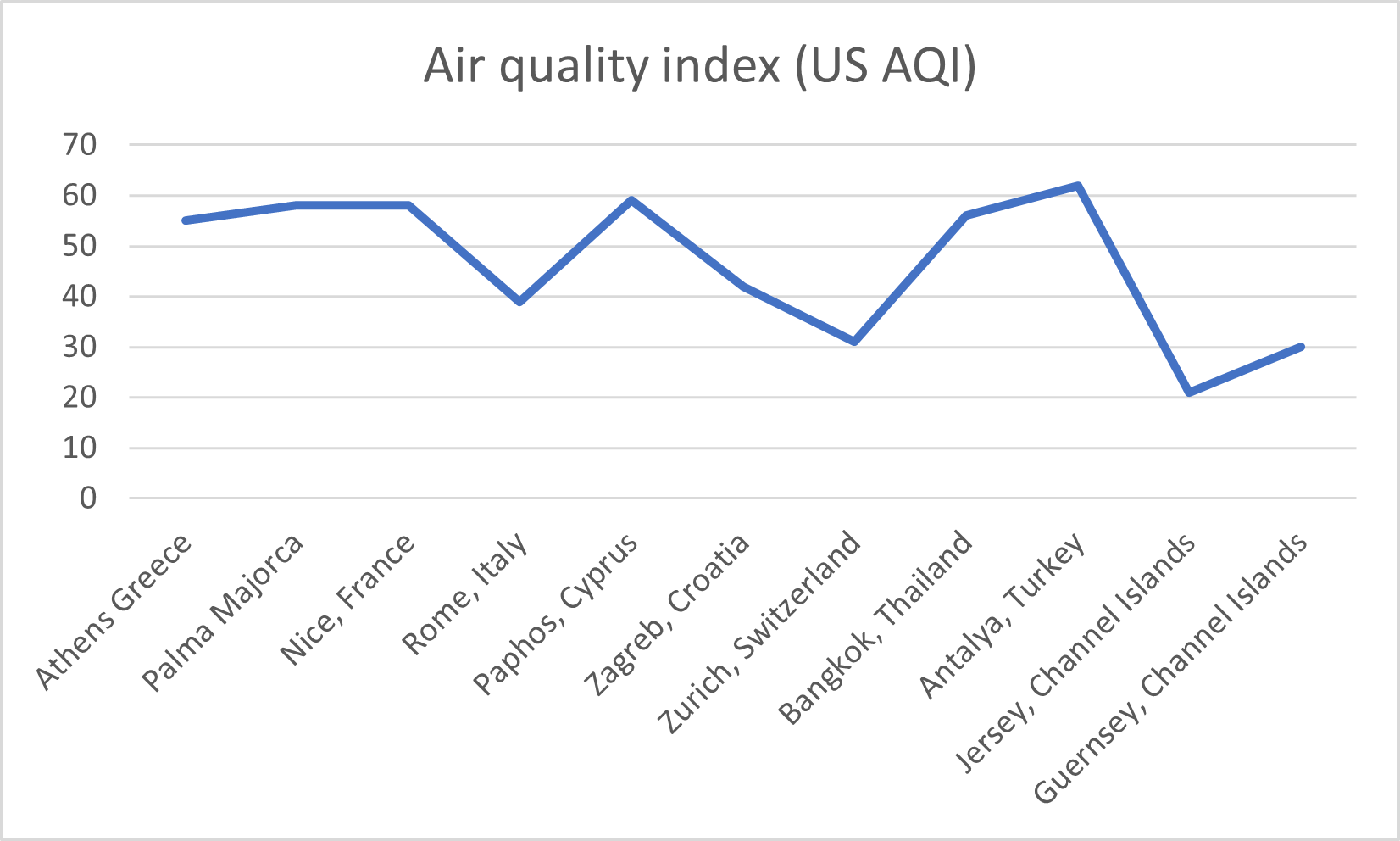
The air quality in the Channel Islands is rated as good, with levels of PM2.5 being lower than other popular holiday destinations. The location of the islands, weather conditions and limited industrial and manufacturing processes all contribute to lower levels. During COVID, the air quality in Jersey improved by 13.6% compared with 2019, due to the lower usage of vehicles.
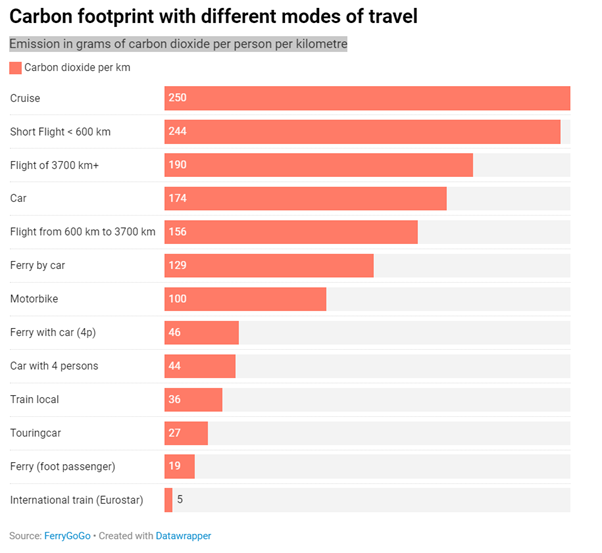
How you choose to travel to a particular destination will also contribute to air pollution. Around 2.4% of global CO2 emissions come from aviation. The aviation industry is also responsible for around 5% of global warming.
Compared to other modes of transport, ferry travel can help reduce your carbon footprint – especially if you travel as a foot passenger.
Air pollution is one of the top threats to global health, beaten only by high blood pressure.
Studies show that nine out of ten people breathe polluted air globally.
48% of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is attributed to air pollution and air pollution causes about 25% of COPD deaths worldwide.
WHO estimates that air pollution causes about 16% of lung cancer deaths worldwide.
It causes about 26% of respiratory infection deaths worldwide.
Other diseases that air pollution can cause include Type 2 diabetes, Obesity, Systemic inflammation, Alzheimer's disease, and Dementia.
Overall death rates from air pollution have dropped by 46% from 1990 to 2021, however the total no. of deaths caused by ambient particulate matter rose 93% from 1990 to 2021.
Around 52% of deaths caused by fine particulate and ozone air pollution are related to cardiometabolic conditions, particularly ischaemic heart disease (30%).
Stroke and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease both account for 16% of mortality burden.
Particulate air pollution takes 2.2 years off global average life expectancy, or a combined 17 billion life-years.
The impact on life expectancy is comparable to that of smoking, more than 3 times that of alcohol use and unsafe water, six times that of HIV/AIDS, and 89 times that of conflict and terrorism.
How many children are affected by air pollution?
8.43 million premature deaths are attributed to air pollution annually.
89% of those premature deaths occurred in low- and middle-income countries.
34% of premature births in 2021 were attributed to exposure to air pollution.
700,000 deaths in children under 5 years were linked to air pollution.
This represents 15% of all global deaths in children under five.
It means, every day almost 2000 children under 5 years die because of health impacts linked to air pollution.
570,000 children under 5 years die from respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, caused by indoor and outdoor air pollution, and second-hand smoke.
Air pollution was the second largest risk factor of death for children under five in 2021.
According to the World Health Organization, air pollution kills an estimated seven million people worldwide each year.
Air pollution is a silent killer. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) reports that by 2050, air pollution in cities, will have become the leading environmental cause of mortality in the world.
There is growing evidence to show air pollution—even when experienced at very low levels—hurts human health. This recently led the World Health Organization (WHO) to revise its guidelines (from 10 µg/m³ to 5 µg/m³) for what it considers a safe level of exposure of particulate pollution. This brings most of the world—97.3% of the global population—into the unsafe zone.
Sources: WHO, Clean Air Fund, Health Data, Unicef, BMJ,
13% of people surveyed check the air quality of a destination before visiting.
21 % of Gen Z travellers are the most likely to check air quality, compared with just 6% of baby boomers.
58% of people surveyed said they had previously experienced breathing difficulties when travelling.
For 34%, breathing problems were made worse by air pollution and dust allergies.
33% suffered from hay fever while 19% had asthma.
17% reported experiencing breathing problems due to air pollution.
It’s estimated UK holidaymakers spend over £998 million a year buying over-the-counter treatments for respiratory or allergy-related illnesses on holiday.
21% of Londoners will check air quality before departure, the highest of any UK region.
High pollution levels cause impaired visibility, health concerns, and a decline in outdoor activities, resulting in a 7.4% drop in tourism, or $1.7 billion in annual losses.
It’s recommended that travellers who are sensitive to air pollution should actively try to avoid destinations with PM2.5 concentrations of more than 15 µg/m3.
Air pollution has an important effect on tourism, influencing travelers’ experiences and limiting the possibility of making trips to certain destinations again. However, tourism also has a negative impact on air pollution.
When air pollution rises by 1%, the number of inbound tourists decreases by approximately 1.171%. Tourists contribute to air pollution through their mobility choices, and the more popular a tourist destination, the more air pollution rises. Travellers choosing more sustainable activities, methods of transport or green hotels, can help to reduce the impact.
Tourism contributes to climate change, and global warming has a profound impact on the industry. Destinations, such as the Maldives face rising sea levels, while the Great Barrier Reef is endangered coral bleaching due to warmer oceans. Ski Resorts are struggling with shorter seasons due to declining snowfall. This reciprocal relationship between tourism and climate change highlights the need for sustainable practices within the travel industry.
Source: Avanti, Gov.je, Oizom, National Library of Medicine
It’s estimated that global cost of health damages associated with exposure to air pollution is $8.1 trillion, equivalent to 6.1 percent of global GDP.
1.2 billion working days lost globally each year.
Every $1 spent on air pollution control yields an estimated $30 in economic benefits.
Air pollution can impact the economy by affecting businesses through a reduction in employees or a rise in sick leave. It also causes premature death, lower crop yields, and impacts tourism, all of which have a knock-on effect on the economy.
Sources: World Bank, OECD, US EPA


